Blood culture and early correct antibacterial treatment are considered priority measures. The rapid and accurate identification of bacteria or fungi that cause bloodstream infections can provide extremely important clinical information for the diagnosis and treatment of sepsis. Clinicians, especially intensive care doctors, deal with infections and antibiotics almost every day. The importance of blood culture is beyond doubt, but do you really understand "blood culture"?
When will blood culture be conducted?
When there is suspicion of bloodstream infection or sepsis, routine blood culture should be performed. Suspected symptoms of bloodstream infection in the patient include:
■ Unexplained fever (>38 ℃) or hypothermia (<36 ℃)
Shock, chills, stiffness
■ Severe local infection (meningitis, Endocarditis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, abdominal postoperative infection...)
■ Abnormal acceleration of heart rate
■ Hypotension or high blood pressure
■ Increased respiratory rate
How to collect blood culture specimens? Key points for high-quality specimen collection:
Firstly, check the blood culture bottle for signs of damage or contamination. Do not use bottles that exhibit turbidity or exceed air pressure, as these may be signs of contamination
■ Check the expiration date printed on each bottle and discard those that have expired
Blood culture bottles should be clearly and correctly labeled
Each pair of bottle blood cultures should be taken from different parts of the body
The blood used for cultivation should be venous blood rather than arterial blood
■ It is recommended to avoid drawing blood from veins or Ductus arteriosus, as these devices usually have a high contamination rate9
Skin disinfection before specimen collection is very important
Send the specimens to the clinical microbiology laboratory for cultivation as soon as possible (preferably within 2 hours). If there is any delay, it should be temporarily stored at room temperature
All blood culture bottles should indicate the patient's condition (including date, time, sampling location, and diagnosis)
How to disinfect skin and blood culture bottles?
The skin disinfection method recommended by CLSI in the United States is: first determine the Venipuncture point, first sterilize with 70% isopropanol and wait for drying, then sterilize with main disinfectants (chlorhexidine, iodine tincture, iodophor) and wait for drying, and the whole process requires strict Aseptic technique.
Disinfection method for blood culture bottles: Discard the plastic cap on the top of the bottle, disinfect the rubber stopper on the top of the bottle with 75% ethanol, and let it dry for 60 seconds.
Some questions about blood collection:
1. It is recommended to collect blood from peripheral veins for blood culture, but arterial blood is not recommended: there is no significant difference in the detection results, but the risk of arterial puncture is relatively high.
2. Routine blood culture should not be taken from venous catheters or venous indwelling devices: there is a high possibility of contamination or colonization of bacteria, unless CRBSI is suspected
3. If blood needs to be taken from the catheter, does the initial blood or fluid replacement inside the catheter need to be discarded? It cannot be discarded to facilitate the identification of contaminated bacteria, colonized bacteria, or
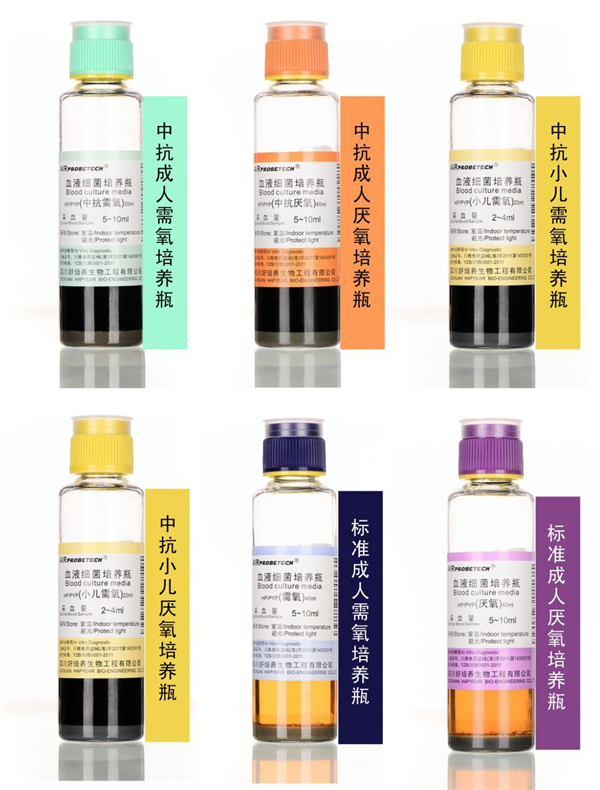

How to choose a culture medium?
According to the recommendation, a routine blood culture for an adult should include a pair of aerobic and anaerobic bottles. The extracted blood should be evenly divided into two parts and injected into aerobic and anaerobic bottles respectively. If anaerobic bottles are not used, an aerobic bottle should be added to ensure sufficient blood volume for cultivation.
What are the requirements and limitations for selecting which bottle to use for pleural and ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, joint cavity fluid, etc?
Sterile body fluid samples such as pleural and ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and joint fluid can be selected from all culture bottles except for MB bottles and children's bottles. In the blood culture of sterile body fluids such as pleural effusion, ascites, cerebrospinal fluid, joint fluid, etc., considering the nutritional requirements of some microorganisms, it may be necessary to add blood or other supplements to promote their growth, especially for those fastidious microorganisms, such as Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc. To ensure the optimal separation rate of these microorganisms, it is recommended to add at least 5ml of blood.
Children's dedicated blood culture bottle:
Attention when receiving: yellow label; Specially designed for children, the blood collection volume is only 2-4 ml; Add special factors to promote bacterial growth, using resin or activated carbon; Low SPS concentration can increase the detection rate of characteristic pathogenic bacteria such as Neisseria in children.
A large amount of blood collection will increase the detection rate of blood culture, but it should be noted that the maximum blood volume of adult blood culture bottles is 10ml/bottle, and the maximum blood volume of PF bottles is 4ml/bottle. Excessive blood volume in the blood culture bottle, exceeding the specified range, may lead to false positives.
How many combinations do blood culture studies require?
Due to the fact that bacteria and fungi cannot always exist in the blood, the sensitivity of individual blood culture combinations is limited. The research shows that the combination of aerobic bottle and anaerobic bottle can detect more staphylococci, some bacteria and causticians in Enterobacteriaceae than a pair of aerobic bottles. If only aerobic bacteria are cultured without anaerobic bacteria, 19% of the strains will not be detected, and another 5% of blood cultures will be delayed by one day to report positive results.
A venous puncture point can only collect one set of blood culture, and the second venous puncture point should be selected for collecting the second set of blood culture.
Although anaerobic infections in children are rare, there are still cases of anaerobic infections in clinical practice. Therefore, in order to obtain more accurate data, it is recommended to use both aerobic and anaerobic bottles for children.
We should also not do a single bottle of blood culture for adults, which will lead to insufficient blood needed for culture, and the existing Bloodstream infections will be missed.
For each sepsis patient, blood should be collected from different parts of the body, and it is usually recommended to collect the required amount of blood from 2 or preferably 3 pairs of blood culture bottles.
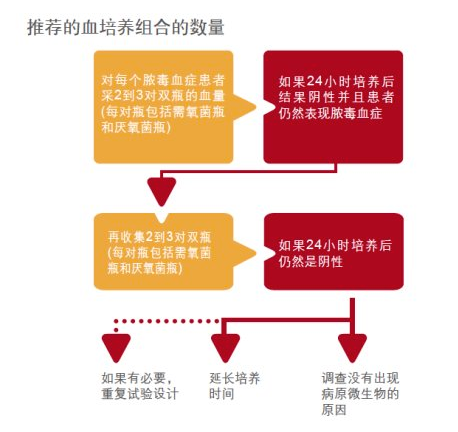
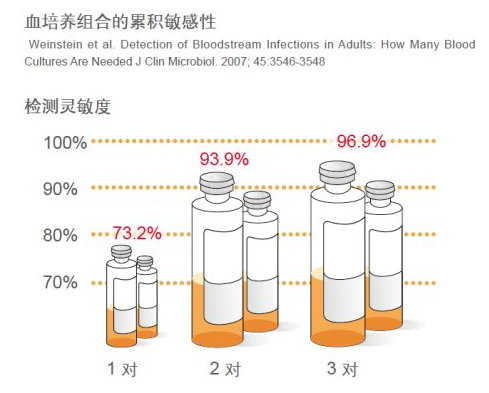
How long will it take to cultivate?
The current recommended standard culture time is five days, which is the routine blood culture time completed by the continuous blood culture monitoring system.
However, published data suggests that three days may be enough to detect clinically significant microorganisms, with a detection rate of 95% -97%.
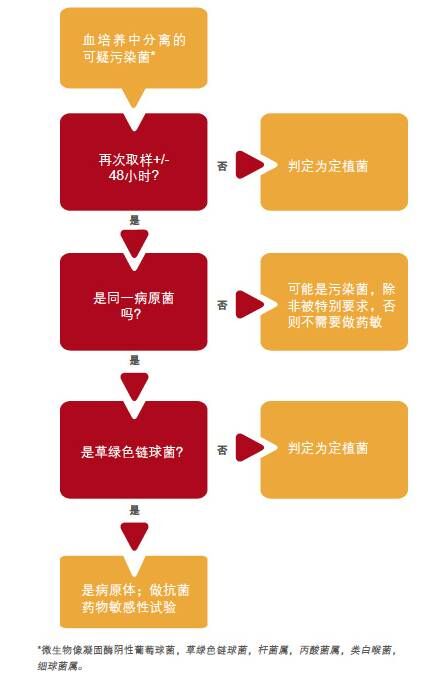
Is it a pollutant or a pathogen?
Determine blood culture contamination based on laboratory rules
Adapted from Richter et al. Minimizing the workup of blood culture contaminants: implementation and evluation of a laboratory-based algorithm. J Clin Microbiol